What is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no external noise is present. These sounds can vary, including ringing, buzzing, hissing, whistling, or humming. While tinnitus itself isn’t a disease, it can be a symptom of an underlying condition or an indicator of changes in the auditory system.
Tinnitus can occur in one or both ears, and it may be constant or intermittent. For some people, it’s barely noticeable, but for others, it can interfere with concentration, sleep, and emotional well-being.


Symptoms of Tinnitus
The hallmark symptom of tinnitus is hearing phantom sounds. However, the specific characteristics can differ from person to person:
- Pitch and tone: Sounds may be high-pitched or low-pitched.
- Volume: The noise can fluctuate or remain at a consistent volume.
- Timing: Some experience tinnitus as a constant sound, while others notice it in quieter environments, such as before bed.
If tinnitus is accompanied by other symptoms like hearing loss, dizziness, or ear pain, it’s essential to seek medical advice to rule out underlying issues.




What Causes Tinnitus?
Tinnitus has many potential causes, and identifying the root is key to effective management. Common causes include:
- Exposure to loud noises: Prolonged exposure to loud environments, such as concerts or machinery, can damage the delicate hair cells in the inner ear, leading to tinnitus.
- Hearing loss: Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis) often accompanies tinnitus, as changes in the auditory system can trigger phantom sounds.
- Ear infections or blockages: A buildup of earwax or an ear infection can alter how sound is processed, potentially causing tinnitus.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as some antibiotics, diuretics, and chemotherapy drugs, list tinnitus as a potential side effect.
- Stress and anxiety: Emotional stress can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms, creating a vicious cycle of discomfort.
- Health conditions: Conditions like Meniere’s disease, high blood pressure, or head and neck injuries are linked to tinnitus.


Managing and Treating Tinnitus
While there is no universal cure for tinnitus, several strategies can help manage its impact and reduce symptoms:
- Hearing aids: If tinnitus is linked to hearing loss, hearing aids can amplify external sounds, reducing the perception of phantom noises.
- Sound therapy: Background noise, such as white noise or nature sounds, can mask tinnitus and make it less intrusive.
- Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT): Learning to manage emotional responses to tinnitus can significantly improve quality of life.
- Relaxation techniques: Mindfulness, yoga, or breathing exercises can help reduce stress, which often worsens tinnitus.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Avoiding loud environments, reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, and maintaining a healthy diet can positively affect symptoms.





When to Seek Help
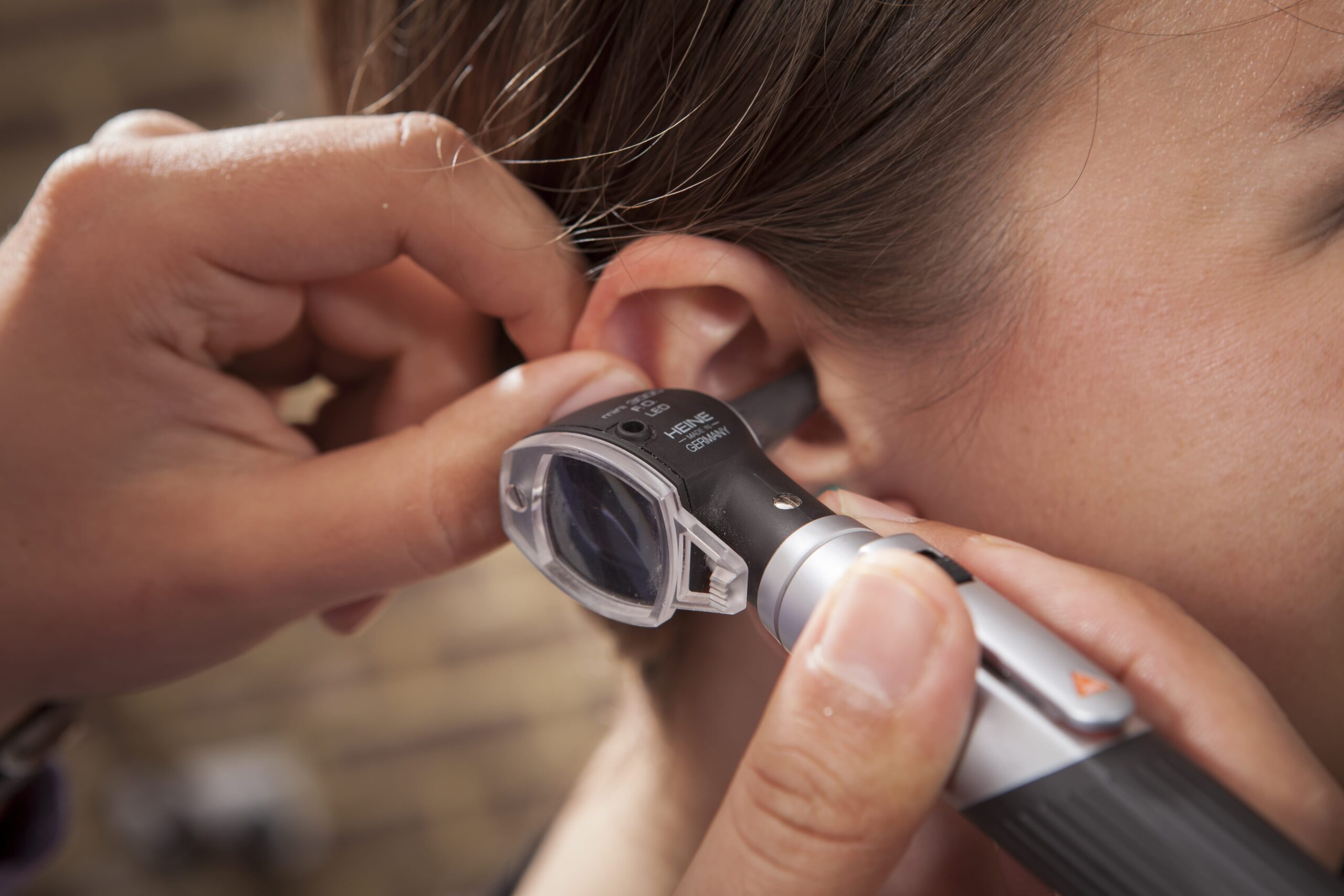
If tinnitus is persistent, worsening, or accompanied by other symptoms like hearing loss or dizziness, professional advice is essential. Regular hearing tests are an excellent first step in assessing your auditory health and understanding the possible causes of tinnitus.
At our Chapman Opticians, we partner with THCP and Diamond Hearing Care Services to provide comprehensive hearing assessments and expert advice on managing tinnitus.




Both myself and my husband use this opticians. The staff are very friendly and helpful. Would definitely recommend to anyone.
Carol Thompson
